Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Andreas Wiese
Research Interests
- Combinatorial optimization
- Approximation algorithms
- Operations research
- Packing problems
- Geometric problems
- Scheduling
Current projects
Automatic course planning with the StudyPlanner
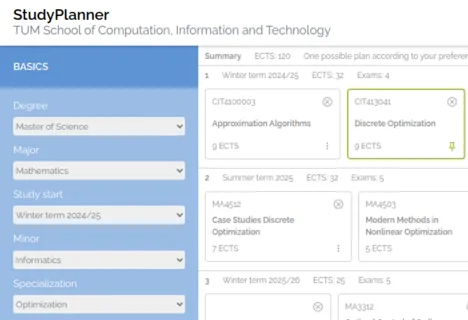
At the beginning of each semester, all university students need to plan the courses they want to take this semester. For this, they need to take into account the rules of their degree program, e.g., some courses are compulsory, one needs to complete a certain number of credits from certain groups of courses, or one needs to choose a study focus from some given options. Also, they need to keep in mind the times when the courses are scheduled, that some courses need to be taken in a certain order, and which courses will be offered in the next semesters. Therefore, this planning process is complicated and tedious.
To help our students, we develop the StudyPlanner in our group which is an online tool with which our students can plan their courses students according to their preferences, from the upcoming semester until the end of their studies, such that all degree rules are automatically fulfilled.
The StudyPlanner is available at studyplanner.co.cit.tum.de.
Assigning teachers to high schools

Each year, the employees of the Bavarian State Ministry for Education need to assign newly hired teachers and trainee teacher to the high schools in Bavaria. For this, they need to take into account the subjects of the teachers, the teacher's preferences which city they want to be assigned to, and the demands of the school. There are many teachers that need to be assigned and, hence, this is a complicated task.
In our group, we develop an automated system that helps the employees of the ministry making these difficult decisions. The goal is that this system computes an assignments that satisfying all rules and which incorporates the teacher's wishes as much as possible. This would save a lot of work for the Ministry's employees and help that the teachers get assigned to a school according to their wishes.
Approximation algorithms for throughput maximization
in collaboration with the group of Fabrizio Grandoni
A well-studied problem setting in combinatorial optimization is to find a way to use limited resources in an optimal way. An important aspect of this is to optimize the throughput in a given system. One example for this are machines in a factory that are used for producing goods. Buying new machines is expensive; therefore, one seeks to utilize the existing machines in the best way possible. Another example is assigning tasks to staff members. Hiring new employees is costly and in some cases not even possible (e.g., due to labour shortage). Therefore, one is interested in assigning the tasks one needs to do in an optimal way to the existing staff members. In this project, we want to develop approximation algorithms for throughput maximization problems, i.e., polynomial time algorithms that compute solutions with a mathematical provable worst-case guarantee for these problems. In particular, we want to investigate relevant throughput maximization settings which are not very well understood at the moment, such as tasks with time windows and multiple resources that are shared among the tasks, possibly across several machines.
Planning of exam supervision and grading
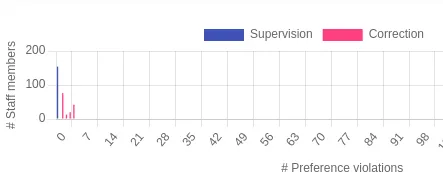
At the end of each semester, the students at TUM write the final exams of their courses. The exams are supervised and graded by employees of TUM. Therefore, one needs to decide which employees supervise and grade each exam. At the Department of Mathematics at TUM this is a quite complicated task, in particular since there are many math exams for other degrees, e.g., engineering or computer science, and not necessarily all exams are supervised or graded by the employees who are in charge of the respective lecture.
Therefore, we develop a system that computes this assignment automatically and also considers wishes of employees such as preferences to supervise or grade certain lectures, days when they are not available, and languages they speak. We hope that this will make the planning process easier and that fewer changes will be necessary afterwards.
University timetabling
in collaboration with the group of Clemens Thielen

A common challenge for a university is to make a schedule for its courses, i.e., to plan for each course at what time and in which lecture hall it takes place. In particular, one must ensure that certain lectures cannot take place at the same time, e.g., two compulsory lectures from the same semester of some study program, that the lecture halls have enough capacity for their assigned courses, and that each lecturer teaches a course only at a time when she is available. Also, ideally one would like to avoid very long breaks for the students during the day and too many lectures being scheduled at undesirable times, e.g., Fridays at 6pm. This leads to a complicated optimization problem. In this project, we solve it for the TUM Campus Straubing.
Position assignment
When a TUM employee is hired, she needs to be assigned to a position among those that are available for TUM. However, sometimes positions are only available during a certain time period or are partially blocked by other employees. Therefore, sometimes it is necessary to find several parts of available positions and combine them together in a suitable way. In the process, one needs to consider the pay grade of the employee and the position and other factors. In this project, we develop an optimization tool that does this process automatically, taking all relevant factors into account. We develop it in collaboration with our colleagues in the adminstration of the School of Computation, Information, and Technology (CIT) in order to help them in the onboarding process of new employees.
Short CV
- since 2022 W3-Associate professor at the Technical University of Munich
- 2021 - 2022 Associate professor at the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam
- 2019 - 2021 Associate professor at the Universidad de Chile in Santiago
- 2016 - 2019 Adjoint professor at the Universidad de Chile in Santiago
- 2012 - 2016 Senior researcher and postdoc at the Max-Planck Institut for Informatics in Saarbrücken/Germany
- 2011 - 2012 Postdoc at the Università di Roma “La Sapienza”
- 2008 - 2011 Ph.D. at TU Berlin under supervision of Martin Skutella
- 2002 - 2008 Study of mathematics and computer science at TU Berlin
Selected publications
- Moritz Buchem, Katja Ettmayr, Hugo K. Rosado, Andreas Wiese. A (3 + ɛ)-approximation algorithm for the minimum sum of radii problem with outliers and extensions for generalized lower bounds. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms (SODA 2024), pages 1738-1765. SIAM 2024.
- Alexander Armbruster, Lars Rohwedder and Andreas Wiese. A PTAS for minimizing weighted flow time on a single machine. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC 2023), pages 1335-1344. ACM, 2023.
- Fabrizio Grandoni, Tobias Mömke, and Andreas Wiese. A PTAS for the Unsplittable Flow on a Path problem. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC 2022), pages 289-302. ACM, 2022.
- Lars Rohwedder and Andreas Wiese. A (2+ ε)-approximation algorithm for preemptive weighted flow time on a single machine. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC 2021), pages 1042-1055. ACM, 2021.
- Fabrizio Grandoni, Tobias Mömke, and Andreas Wiese. Unsplittable Flow on a Path: The Game! In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms (SODA 2022), pages 906-926. SIAM 2022.
- Anna Adamaszek, Sariel Har-Peled, and Andreas Wiese. Approximation Schemes for Independent Set and Sparse Subsets of Polygons. In Journal of the ACM 66(4): 29:1-29:40 (2019). Unifies in particular two extended abstracts published in FOCS 2013 and SODA 2014.
- Fabrizio Grandoni, Tobias Mömke, Andreas Wiese, and Hang Zhou. A (5/3+ ε) -approximation for unsplittable flow on a path: placing small tasks into boxes. In Proceedings of the 50th Annual Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC 2018), pages 607-619. ACM, 2018.
- Sandy Heydrich and Andreas Wiese. Faster approximation schemes for the two-dimensional knapsack problem. ACM Transactions on Algorithms 15: 47:1-47:28 (2019). An extended abstract was published in SODA 2017
- Waldo Gálvez, Fabrizio Grandoni, Sandy Heydrich, Salvatore Ingala, Arindam Khan and Andreas Wiese: Approximating Geometric Knapsack via L-Packings. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS 2017), pages 260-271. IEEE, 2017
- Giorgi Nadiradze and Andreas Wiese. On approximating strip packing with a better ratio than 3/2. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms (SODA 2016), pages 1491-1510. SIAM 2016.
- Anna Adamaszek and Andreas Wiese. A quasi-PTAS for the two-dimensional geometric knapsack problem. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms (SODA 2015), pages 149-1505. SIAM 2015.
- Paul Bonsma, Jens Schulz, and Andreas. Wiese. A constant-factor approximation algorithm for unsplittable flow on paths. SIAM Journal on Computing, 43:767–799, 2014. An extended abstract appeared in the proceedings of FOCS 2011.
Service to the academic community
- Co-organizer of the 16th Latin American Theoretical Informatics Symposium (LATIN 2024)
- Program committee member of SOSA 2026, STACS 2025, LATIN 2024 (co-PC-chair), ICALP 2024, WAOA 2023 (co-PC-chair), FOCS 2023, STOC 2023, SODA 2023, ESA 2022, SODA 2022, SoCG 2022, LAGOS 2021, ESA 2020, WAOA 2019, SODA 2018, LATIN 2018, CIAC 2017, ESA 2015, APPROX 2015, WAOA 2015, WAOA 2014, MAPSP 2013, and WAOA 2012
- Organizer and co-organizer of an annual research workshop at the Universidad de Chile during 2016-2022
- Co-organizer of the “Summer school in discrete mathematics 2018" in Valparaíso/Chile
- Organizer of the summer school ADFOCS 2015 at MPI for Informatics in Saarbrücken/Germany
- Reviewer for the German Research Foundation (DFG), the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), the Israel Science Foundation (ISF), the Comisión Nacional de Investigación Científica y Tecnológica (CONICYT) in Chile, and the National Science Centre Poland
Supervision
Postdocs (current and previous)
- Ruilong Zhang
- Moritz Buchem
- Hugo Kasuya
- Kevin Schewior
- Syamantak Das
- Hang Zhou
PhD students (current and previous)
- Alexander Armbruster
- Elisa Dell'Arriva (one year visit)
- Sandy Heydrich (co-advised with Rob van Stee)
Recent courses
Miscellaneous material
- Tips for giving a good scientific talk
- How to do well in a student seminar
- How to write a bachelor/master thesis
- MIP coding cookbook (with Python and Pyomo)
- The ski rental problem with advice as a game (programmed by my seminar student Larissa Rickler)
- The k-server problem with advice as a game (programmed by my seminar student Daniel Manny)